using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.ComponentModel; using System.Xml.Linq; namespace SetOperators { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { LinqSamples samples = new LinqSamples(); //Comment or uncomment the method calls below to run or not samples.Linq46(); // This sample uses Distinct to remove duplicate elements in a sequence of factors of 300 //samples.Linq47(); // This sample uses Distinct to find the unique Category names //samples.Linq48(); // This sample uses Union to create one sequence that contains the unique values from both // arrays //samples.Linq49(); // This sample uses the Union method to create one sequence that contains the unique first // letter from both product and customer names. Union is only available through method // syntax //samples.Linq50(); // This sample uses Intersect to create one sequence that contains the common values shared // by both arrays //samples.Linq51(); // This sample uses Intersect to create one sequence that contains the common first letter // from both product and customer names //samples.Linq52(); // This sample uses Except to create a sequence that contains the values from numbersA that // are not also in numbersB //samples.Linq53(); // This sample uses Except to create one sequence that contains the 1st letters of product // names that are not also first letters of customer names } public class Product { public int ProductID { get; set; } public string ProductName { get; set; } public string Category { get; set; } public decimal UnitPrice { get; set; } public int UnitsInStock { get; set; } } public class Order { public int OrderID { get; set; } public DateTime OrderDate { get; set; } public decimal Total { get; set; } } public class Customer { public string CustomerID { get; set; } public string CompanyName { get; set; } public string Address { get; set; } public string City { get; set; } public string Region { get; set; } public string PostalCode { get; set; } public string Country { get; set; } public string Phone { get; set; } public string Fax { get; set; } public Order[] Orders { get; set; } } class LinqSamples { private List<Product> productList; private List<Customer> customerList; [Category("Set Operators")] [Description("This sample uses Distinct to remove duplicate elements in a sequence of " + "factors of 300.")] public void Linq46() { int[] factorsOf300 = { 2, 2, 3, 5, 5 }; var uniqueFactors = factorsOf300.Distinct(); Console.WriteLine("Prime factors of 300:"); foreach (var f in uniqueFactors) { Console.WriteLine(f); } } [Category("Set Operators")] [Description("This sample uses Distinct to find the unique Category names.")] public void Linq47() { List<Product> products = GetProductList(); var categoryNames = ( from prod in products select prod.Category) .Distinct(); Console.WriteLine("Category names:"); foreach (var n in categoryNames) { Console.WriteLine(n); } } [Category("Set Operators")] [Description("This sample uses Union to create one sequence that contains the unique values " + "from both arrays.")] public void Linq48() { int[] numbersA = { 0, 2, 4, 5, 6, 8, 9 }; int[] numbersB = { 1, 3, 5, 7, 8 }; var uniqueNumbers = numbersA.Union(numbersB); Console.WriteLine("Unique numbers from both arrays:"); foreach (var n in uniqueNumbers) { Console.WriteLine(n); } } [Category("Set Operators")] [Description("This sample uses the Union method to create one sequence that contains the unique first letter " + "from both product and customer names. Union is only available through method syntax.")] public void Linq49() { List<Product> products = GetProductList(); List<Customer> customers = GetCustomerList(); var productFirstChars = from prod in products select prod.ProductName[0]; var customerFirstChars = from cust in customers select cust.CompanyName[0]; var uniqueFirstChars = productFirstChars.Union(customerFirstChars); Console.WriteLine("Unique first letters from Product names and Customer names:"); foreach (var ch in uniqueFirstChars) { Console.WriteLine(ch); } } [Category("Set Operators")] [Description("This sample uses Intersect to create one sequence that contains the common values " + "shared by both arrays.")] public void Linq50() { int[] numbersA = { 0, 2, 4, 5, 6, 8, 9 }; int[] numbersB = { 1, 3, 5, 7, 8 }; var commonNumbers = numbersA.Intersect(numbersB); Console.WriteLine("Common numbers shared by both arrays:"); foreach (var n in commonNumbers) { Console.WriteLine(n); } } [Category("Set Operators")] [Description("This sample uses Intersect to create one sequence that contains the common first letter " + "from both product and customer names.")] public void Linq51() { List<Product> products = GetProductList(); List<Customer> customers = GetCustomerList(); var productFirstChars = from prod in products select prod.ProductName[0]; var customerFirstChars = from cust in customers select cust.CompanyName[0]; var commonFirstChars = productFirstChars.Intersect(customerFirstChars); Console.WriteLine("Common first letters from Product names and Customer names:"); foreach (var ch in commonFirstChars) { Console.WriteLine(ch); } } [Category("Set Operators")] [Description("This sample uses Except to create a sequence that contains the values from numbersA" + "that are not also in numbersB.")] public void Linq52() { int[] numbersA = { 0, 2, 4, 5, 6, 8, 9 }; int[] numbersB = { 1, 3, 5, 7, 8 }; IEnumerable<int> aOnlyNumbers = numbersA.Except(numbersB); Console.WriteLine("Numbers in first array but not second array:"); foreach (var n in aOnlyNumbers) { Console.WriteLine(n); } } [Category("Set Operators")] [Description("This sample uses Except to create one sequence that contains the first letters " + "of product names that are not also first letters of customer names.")] public void Linq53() { List<Product> products = GetProductList(); List<Customer> customers = GetCustomerList(); var productFirstChars = from prod in products select prod.ProductName[0]; var customerFirstChars = from cust in customers select cust.CompanyName[0]; var productOnlyFirstChars = productFirstChars.Except(customerFirstChars); Console.WriteLine("First letters from Product names, but not from Customer names:"); foreach (var ch in productOnlyFirstChars) { Console.WriteLine(ch); } } public List<Product> GetProductList() { if (productList == null) createLists(); return productList; } public List<Customer> GetCustomerList() { if (customerList == null) createLists(); return customerList; } private void createLists() { // Product data created in-memory using collection initializer: productList = new List<Product> { new Product { ProductID = 1, ProductName = "Chai", Category = "Beverages", UnitPrice = 18.0000M, UnitsInStock = 39 }, new Product { ProductID = 2, ProductName = "Chang", Category = "Beverages", UnitPrice = 19.0000M, UnitsInStock = 17 }, new Product { ProductID = 3, ProductName = "Aniseed Syrup", Category = "Condiments", UnitPrice = 10.0000M, UnitsInStock = 13 }, new Product { ProductID = 4, ProductName = "Chef Anton's Cajun Seasoning", Category = "Condiments", UnitPrice = 22.0000M, UnitsInStock = 53 }, new Product { ProductID = 5, ProductName = "Chef Anton's Gumbo Mix", Category = "Condiments", UnitPrice = 21.3500M, UnitsInStock = 0 } }; // Customer/Order data read into memory from XML file using XLinq: customerList = ( from e in XDocument.Load("Customers.xml"). Root.Elements("customer") select new Customer { CustomerID = (string)e.Element("id"), CompanyName = (string)e.Element("name"), Address = (string)e.Element("address"), City = (string)e.Element("city"), Region = (string)e.Element("region"), PostalCode = (string)e.Element("postalcode"), Country = (string)e.Element("country"), Phone = (string)e.Element("phone"), Fax = (string)e.Element("fax"), Orders = ( from o in e.Elements("orders").Elements("order") select new Order { OrderID = (int)o.Element("id"), OrderDate = (DateTime)o.Element("orderdate"), Total = (decimal)o.Element("total") }) .ToArray() }) .ToList(); } } } }
Sunday, 29 June 2014
LINQ - Set Operators
Tuesday, 25 September 2012
Edit csproj.cs file programmatically using c#
private void IncludeFilesInProject(string csProjName, string tagContent)
{
string csprojPath = txtdefaultPath.Text + "\\" + csProjName;
XmlDocument myXmlDocument = new XmlDocument();
myXmlDocument.Load(csprojPath);
XmlTextReader reader = new XmlTextReader(csprojPath);
XmlDocument doc = new XmlDocument();
doc.Load(reader);
reader.Close();
XmlNode currNode;
XmlDocumentFragment docFrag = doc.CreateDocumentFragment();
docFrag.InnerXml = tagContent;
// insert the availability node into the document
currNode = doc.DocumentElement;
currNode.InsertAfter(docFrag, currNode.LastChild);
//save the output to a file
doc.Save(csprojPath);
//Overwrite the existing file with new file content.
string projFile = File.ReadAllText(csprojPath);
string newProjFile = projFile.Replace(" xmlns=\"\"", "");
File.WriteAllText(csprojPath, newProjFile);
}
{
string csprojPath = txtdefaultPath.Text + "\\" + csProjName;
XmlDocument myXmlDocument = new XmlDocument();
myXmlDocument.Load(csprojPath);
XmlTextReader reader = new XmlTextReader(csprojPath);
XmlDocument doc = new XmlDocument();
doc.Load(reader);
reader.Close();
XmlNode currNode;
XmlDocumentFragment docFrag = doc.CreateDocumentFragment();
docFrag.InnerXml = tagContent;
// insert the availability node into the document
currNode = doc.DocumentElement;
currNode.InsertAfter(docFrag, currNode.LastChild);
//save the output to a file
doc.Save(csprojPath);
//Overwrite the existing file with new file content.
string projFile = File.ReadAllText(csprojPath);
string newProjFile = projFile.Replace(" xmlns=\"\"", "");
File.WriteAllText(csprojPath, newProjFile);
}
Saturday, 22 September 2012
LINQ - Conversion Operators
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.ComponentModel; using System.Xml.Linq; namespace ConversionOperators { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { LinqSamples samples = new LinqSamples(); //Comment or uncomment the method calls below to run or not samples.Linq54(); // This sample uses ToArray to immediately evaluate a sequence into an array //samples.Linq55(); // This sample uses ToList to immediately evaluate a sequence into a List<T> //samples.Linq56(); // This sample uses ToDictionary to immediately evaluate a sequence and a // related key expression into a dictionary //samples.Linq57(); // This sample uses OfType to return only the elements of the array that are // of type double } class LinqSamples { [Category("Conversion Operators")] [Description("This sample uses ToArray to immediately evaluate a sequence into an array.")] public void Linq54() { double[] doubles = { 1.7, 2.3, 1.9, 4.1, 2.9 }; var sortedDoubles = from d in doubles orderby d descending select d; var doublesArray = sortedDoubles.ToArray(); Console.WriteLine("Every other double from highest to lowest:"); for (int d = 0; d < doublesArray.Length; d += 2) { Console.WriteLine(doublesArray[d]); } } [Category("Conversion Operators")] [Description("This sample uses ToList to immediately evaluate a sequence into a List<T>.")] public void Linq55() { string[] words = { "cherry", "apple", "blueberry" }; var sortedWords = from w in words orderby w select w; var wordList = sortedWords.ToList(); Console.WriteLine("The sorted word list:"); foreach (var w in wordList) { Console.WriteLine(w); } } [Category("Conversion Operators")] [Description("This sample uses ToDictionary to immediately evaluate a sequence and a " + "related key expression into a dictionary.")] public void Linq56() { var scoreRecords = new[] { new {Name = "Alice", Score = 50}, new {Name = "Bob" , Score = 40}, new {Name = "Cathy", Score = 45} }; var scoreRecordsDict = scoreRecords.ToDictionary(sr => sr.Name); Console.WriteLine("Bob's score: {0}", scoreRecordsDict["Bob"]); } [Category("Conversion Operators")] [Description("This sample uses OfType to return only the elements of the array that are of type double.")] public void Linq57() { object[] numbers = { null, 1.0, "two", 3, "four", 5, "six", 7.0 }; var doubles = numbers.OfType<double>(); Console.WriteLine("Numbers stored as doubles:"); foreach (var d in doubles) { Console.WriteLine(d); } } } } }
Some Userful links, must share this.....
1. Find an item in List by LINQ?
http://stackoverflow.com/questions/1175645/find-an-item-in-list-by-linq
2. Using LINQ to Objects in C#
http://www.codeproject.com/Articles/26743/Using-LINQ-to-Objects-in-C
3. 101 LINQ Samples
http://code.msdn.microsoft.com/101-LINQ-Samples-3fb9811b
Read Write Edit Word Document In ASP.NET
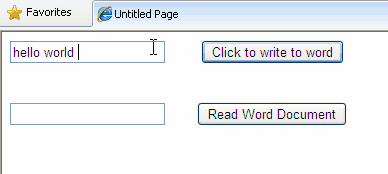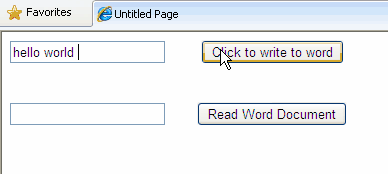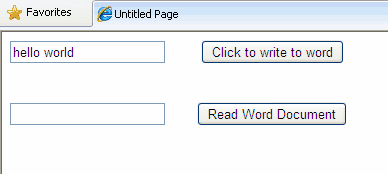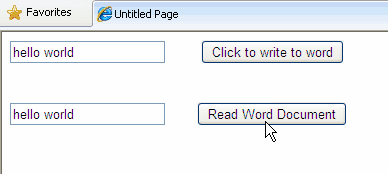
In this article i am explaining how to Read Write Edit Word Document With FileStream StreamWriter In ASP.NET. For this i've added a textbox for input text to be written in word document and a button to write, same for reading text from word file.
The word file created is saved in a folder named document in root of application. which can be changed to desired location.
html source of the page look like
To use Filestream and stringBuilder we need to add these namespace
C# code behind
VB.NET code
The word file created is saved in a folder named document in root of application. which can be changed to desired location.
html source of the page look like
<form id="form1" runat="server">
<div>
<asp:TextBox ID="TextBox1" runat="server">
</asp:TextBox>
<asp:Button ID="Button1" runat="server"
onclick="Button1_Click"
Text="Click to write to word" />
<br />
<asp:TextBox ID="TextBox2" runat="server">
</asp:TextBox>
<asp:Button ID="Button2" runat="server"
onclick="Button2_Click"
Text="Read Word Document" />
</div>
</form>
To use Filestream and stringBuilder we need to add these namespace
using System.IO;
using System.Text;
C# code behind
protected void Button1_Click(object sender, EventArgs e) { //Create stringBuilder to write formatted //Text to word file StringBuilder strBuilder = new StringBuilder(); strBuilder.Append("<h1 title='Header' align='Center'> Writing To Word Using ASP.NET</h1> ".ToString()); strBuilder.Append("<br>".ToString()); strBuilder.Append("<table align='Center'>".ToString()); strBuilder.Append("<tr>".ToString()); strBuilder.Append("<td style='width:100px;color:green'> <b>amiT</b></td>".ToString()); strBuilder.Append("<td style='width:100px;color:red'> India</td>".ToString()); strBuilder.Append("</tr>".ToString()); strBuilder.Append("</table>".ToString()); string strPath = Request.PhysicalApplicationPath + "\\document\\Test.doc"; //string strTextToWrite = TextBox1.Text; FileStream fStream = File.Create(strPath); fStream.Close(); StreamWriter sWriter = new StreamWriter(strPath); Writer.Write(strBuilder); sWriter.Close(); } protected void Button2_Click(object sender, EventArgs e) { string strPath = Request.PhysicalApplicationPath + "\\document\\Test.doc"; FileStream fStream = new FileStream (strPath, FileMode.Open, FileAccess.Read); StreamReader sReader = new StreamReader(fStream); TextBox2.Text = sReader.ReadToEnd(); sReader.Close(); Response.Write(TextBox2.Text); }
VB.NET code
Protected Sub Button1_Click (ByVal sender As Object, ByVal e As EventArgs) Dim strBuilder As New StringBuilder() strBuilder.Append("<h1 title='Header' align='Center'> Writing To Word Using ASP.NET</h1> ".ToString()) strBuilder.Append("<br>".ToString()) strBuilder.Append("<table align='Center'>".ToString()) strBuilder.Append("<tr>".ToString()) strBuilder.Append("<td style='width:100px;color:green'> <b>amiT</b></td>".ToString()) strBuilder.Append("<td style='width:100px;color:red'> India</td>".ToString()) strBuilder.Append("</tr>".ToString()) strBuilder.Append("</table>".ToString()) 'string path = @"C:\Test.doc"; Dim strPath As String = Request.PhysicalApplicationPath & "\document\Test.doc" 'string strTextToWrite = TextBox1.Text; Dim fStream As FileStream = File.Create(strPath) fStream.Close() Dim sWriter As New StreamWriter(strPath) sWriter.Write(strBuilder) sWriter.Close() End Sub Protected Sub Button2_Click (ByVal sender As Object, ByVal e As EventArgs) Dim strPath As String = Request.PhysicalApplicationPath & "\document\Test.doc" Dim fStream As New FileStream (strPath, FileMode.Open, FileAccess.Read) Dim sReader As New StreamReader(fStream) TextBox2.Text = sReader.ReadToEnd() sReader.Close() Response.Write(TextBox2.Text) End Sub
how to read, write, edit, delete using filestream in c#
using System; using System.IO; class Test { public static void Main() { // Specify a file to read from and to create. string pathSource = @"c:\tests\source.txt"; string pathNew = @"c:\tests\newfile.txt"; try { using (FileStream fsSource = new FileStream(pathSource, FileMode.Open, FileAccess.Read)) { // Read the source file into a byte array. byte[] bytes = new byte[fsSource.Length]; int numBytesToRead = (int)fsSource.Length; int numBytesRead = 0; while (numBytesToRead > 0) { // Read may return anything from 0 to numBytesToRead. int n = fsSource.Read(bytes, numBytesRead, numBytesToRead); // Break when the end of the file is reached. if (n == 0) break; numBytesRead += n; numBytesToRead -= n; } numBytesToRead = bytes.Length; // Write the byte array to the other FileStream. using (FileStream fsNew = new FileStream(pathNew, FileMode.Create, FileAccess.Write)) { fsNew.Write(bytes, 0, numBytesToRead); } } } catch (FileNotFoundException ioEx) { Console.WriteLine(ioEx.Message); } } }
Build .Net Project Solution programatically using C#
private void btnBuild_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
richTextBox1.Text = "";
string[] solutions = GetSolutions();
foreach (string solution in solutions)
{
var startinfo = new ProcessStartInfo();
startinfo.FileName = @"C:\Windows\Microsoft.NET\Framework\v4.0.30319\msbuild.exe";
startinfo.Arguments = "/t:rebuild /p:Configuration=Debug " + solution;
startinfo.RedirectStandardError = true;
startinfo.RedirectStandardOutput = true;
startinfo.UseShellExecute = false;
Process build = Process.Start(startinfo);
//string error = build.StandardError.ReadToEnd();
string output = build.StandardOutput.ReadToEnd();
build.WaitForExit();
richTextBox1.Text = output;
}
}
private string[] GetSolutions()
{
string[] filePaths = Directory.GetFiles(txtLoc.Text);
return filePaths;
}
{
richTextBox1.Text = "";
string[] solutions = GetSolutions();
foreach (string solution in solutions)
{
var startinfo = new ProcessStartInfo();
startinfo.FileName = @"C:\Windows\Microsoft.NET\Framework\v4.0.30319\msbuild.exe";
startinfo.Arguments = "/t:rebuild /p:Configuration=Debug " + solution;
startinfo.RedirectStandardError = true;
startinfo.RedirectStandardOutput = true;
startinfo.UseShellExecute = false;
Process build = Process.Start(startinfo);
//string error = build.StandardError.ReadToEnd();
string output = build.StandardOutput.ReadToEnd();
build.WaitForExit();
richTextBox1.Text = output;
}
}
private string[] GetSolutions()
{
string[] filePaths = Directory.GetFiles(txtLoc.Text);
return filePaths;
}
Monday, 10 September 2012
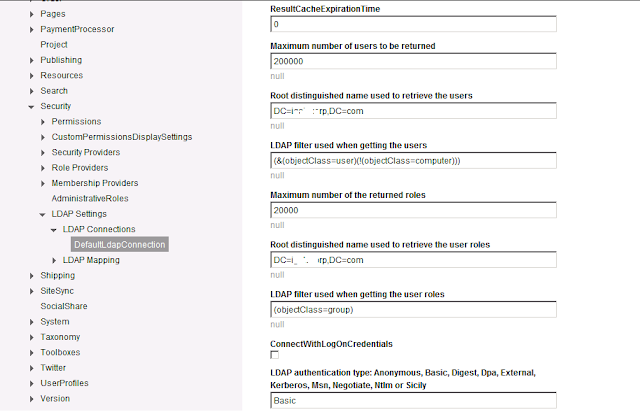
Configuring LDAP in Sitefinity 4.4 in Telerik Sitefinity
Configuring LDAP in Sitefinity 4.4
Windows Active Directory is a directory service created by Microsoft. Active Directory uses a number of standardized protocols to provide a variety of network service, including LDAP. LDAP is Lightweight Directory Access Protocol for accessing directories over an IP network.
You configure LDAP settings in the following way:
- In the main menu, click Administration » Settings.
- The Basic Settings page appears.
- Click, Advanced link.
- The Settings page appears.
- Expand Security node in the left of the page.
- Click LDAP Settings à LDAP Connections.
A list of all configured connections appears. You can edit an existing connection by clicking it or you can create a new connection by clicking Create new button.
Configure the following properties:
Note : All the Fields values may be change according to your LDAP Servers setting.
Name
|
The name of the connection is used for distinguishing LDAP connections in Sitefinity. It should be IP Address of the server where LDAP directory is hosted (Not the machine name / Server Name).
|
ServerName
|
Enter the name of the server where LDAP is hosted.
|
Port
|
Enter the LDAP server port. The default port is 389.
|
ConnectionDomain
|
Enter the domain of the LDAP server.
|
ConnectionUsername
|
Enter the username for logging to the LDAP server.
|
ConnectionPassword
|
Enter the password for logging to the LDAP server.
|
UseSsl
|
Indicates whether the connection use SSL or not
|
ResultCacheExpirationTime
|
Enter the seconds, for which the system caches the LDAP server response results.
|
MaxReturnedUsers
|
Enter the maximum number of users that is returned on one request to the LDAP. This number is used for internal paging of results, in order to avoid overconsumption of memory and slow retrieval of big chunks of data.
|
UserDns
|
Enter the base/root distinguished name (DN) for the users.
|
UserFilter
|
Enter the filter that is applied when requesting users from the LDAP. You must use the standard LDAP query syntax.
|
MaxReturnedRoles
|
Enter the maximum number of roles that is returned on one request to the LDAP. This number is used for internal paging of results, in order to avoid overconsumption of memory and slow retrieval of big chunks of data.
|
RolesDNs
|
Enter the base/root distinguished name (DN) for the roles.
|
RolesFilter
|
Enter the filter applied when requesting users from the LDAP. You must use the standard LDAP query syntax.
|
ConnectWithLogOnCredentials
|
Indicates whether to use current user credentials or those entered above. If you select this checkbox, the LDAP is connected and browsed with the credentials that the user provides on logging into Sitefinity backend and you do not have to enter user and password into the LDAP configuration.
|
AuthenticationType
|
Enter one of the following:
· Basic
Indicates that basic authentication will be used with the connection.
· NTLM
|
- When you are finished with the configurations, click Save changes.
- To select which is the default LDAP connection to be used, click LDAP Settings and enter the name of the connection in DefaultLdapConnection input field and click Save changes button.
When you successfully saved all these settings restart the Sitefinity server and again run the CMS project and check whether the LDAP users and LDAP roles are showing or not in the Users and Roles section of Administration menu.
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)
How to find a string within a jQuery or javascript string
Sometimes, you required to find a the existence of a small string with in a string. This article will demonstarte , how could you do by...
-
In this article i am explaining how to Read Write Edit Word Document With FileStream StreamWriter In ASP.NET . For this i've added a te...
-
IdentityModels.cs public class ApplicationUser : IdentityUser { public string First_Name { get; set; } public string Last_Name { get; se...